Have you ever wondered how the mind can influence how you perceive pain? Pain is a universal human experience, a signal from our bodies that something is not quite right. Yet, the ways in which we can manage and modulate this discomfort can vary widely. One intriguing area of research is the study of mindfulness meditation and its ability to reduce pain. Researchers at UC San Diego recently conducted an illuminating study aimed at understanding the pain-reducing effects of mindfulness meditation compared to placebos. Here’s a deep dive into their findings and what they could mean for the future of pain management.
The Objective of the Study
Researchers embarked on this study to dissect the pain-reducing capabilities of mindfulness meditation and compare them with those of placebo interventions. With chronic pain affecting millions of individuals worldwide, understanding alternative and complementary therapies to pharmaceutical drugs is of essential value.
How Was the Study Conducted?
The study was meticulously designed to provide comprehensive data about the effects of mindfulness meditation on pain.
Participants
A total of 115 participants were enrolled in the study to ensure a broad and varied data set. The participants were divided into several groups, each subjected to a different type of intervention.
The Four Interventions
The participants were divided into four groups, each experiencing one of the following interventions:
- Guided Mindfulness Meditation
- Sham Meditation
- Placebo Cream
- Control Group (Listening to an Audiobook)
These interventions were selected to evaluate the real efficacy of mindfulness mediation by contrasting it against both placebo treatments and a non-intervention control.
Advanced Brain Imaging Techniques
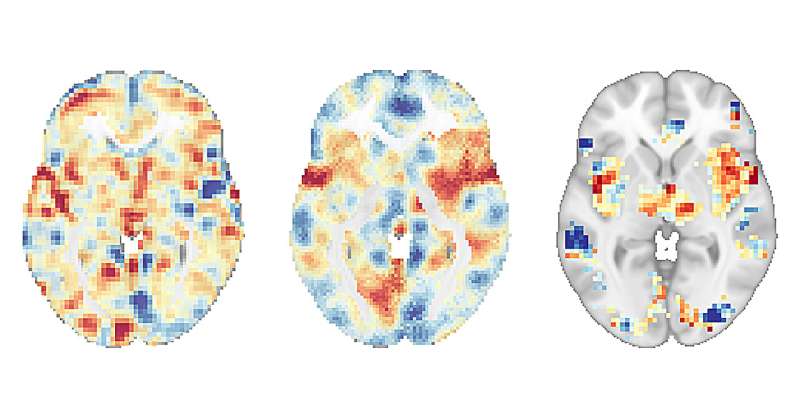
To gain an in-depth understanding, the researchers utilized advanced brain imaging. They specifically used Multivariate Pattern Analysis (MVPA) to assess brain activity in response to a painful heat stimulus.
The Science Behind Pain and the Interventions
Neural Mechanisms and Pain Perception
Pain perception is controlled by complex neural mechanisms. These mechanisms involve brain areas such as the anterior cingulate cortex, insula, and thalamus, which work together to produce the sensation of pain and the accompanying emotional distress.
Mindfulness Meditation: The Mechanisms
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment while calmly acknowledging and accepting one’s feelings, thoughts, and bodily sensations. The practice encourages a non-judgmental awareness of sensory events.
Brain Activity Patterns
During mindfulness meditation, the researchers observed that specific brain activity patterns associated with pain and negative emotions were modulated. This modulation reduces both the intensity of the pain and its unpleasantness.
Placebo Effect: The Mechanisms
The placebo effect, on the other hand, engages brain processes predominantly related to expectations. When individuals believe they are receiving a treatment, their expectation activates certain brain regions that can temporarily reduce the perception of pain. However, it does not alter the underlying pain experience.
Comparing Both Mechanisms
In comparing both mechanisms, it’s clear that mindfulness meditation works differently from placebos. Placebo treatment relies on expectations and does not change the underlying pain experience, while mindfulness meditation appears to directly influence how pain and negative emotions are processed in the brain.
Results and Findings
The outcomes of the study were revealing and promising. Using advanced imaging techniques, researchers observed that participants practicing mindfulness meditation experienced a significant reduction in both pain intensity and pain unpleasantness.
Summary of Study Findings
| Intervention | Pain Intensity Reduction | Pain Unpleasantness Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness Meditation | Significant | Significant |
| Sham Meditation | Moderate | Moderate |
| Placebo Cream | Mild | Mild |
| Control (Audiobook) | None | None |
These results demonstrate that:
- Mindfulness meditation was markedly more effective at reducing pain compared to placebo and sham interventions.
- The placebo effect showed only mild reductions, highlighting the unique effectiveness of mindfulness meditation.
The Implications for Chronic Pain Management
Direct Intervention for Chronic Pain
The study suggests that mindfulness meditation could serve as a direct intervention for patients suffering from chronic pain. By directly influencing brain mechanisms associated with pain and emotional regulation, mindfulness meditation might offer a potent, non-pharmaceutical option for managing chronic pain.
Further Research Needed
While the results are promising, there is a need for further studies to confirm the efficacy of mindfulness meditation specifically in chronic pain patients. Future research will need to explore long-term effects, feasibility in different populations, and integration with other forms of pain management.
Future Directions for Pain Management Therapies
Developing Effective and Accessible Therapies
One of the pivotal aspects of this research is its potential to inform the development of more effective and accessible pain management therapies. With the increasing interest in holistic and integrative medicine, mindfulness meditation could become a cornerstone in modern pain management strategies.
Educating Healthcare Providers and Patients
It’s crucial to educate both healthcare providers and patients about the benefits and methods of mindfulness meditation. This can be achieved through:
- Training workshops
- Educational materials
- Integrating mindfulness practices into standard healthcare protocols
Collaboration With Other Therapeutic Approaches
Mindfulness meditation could also be used in conjunction with other therapeutic approaches, both traditional and alternative, to enhance overall pain management outcomes.
Publication and Contributions
The study was published in the prestigious journal, Biological Psychiatry, reflecting its significance in the field. Contributions came from researchers not only at UC San Diego but also from Dartmouth College. This collaboration underscores the importance of interdisciplinary research in unraveling the complexities of pain and its management.
Conclusion
Even though mindfulness meditation has been practiced for centuries, its potential as a scientifically validated tool for pain reduction is only beginning to be understood in full. The research conducted at UC San Diego opens new avenues for pain management, highlighting that the mind’s power can be harnessed to alleviate physical discomfort. As we move forward, integrating mindfulness meditation into treatment plans could revolutionize how we approach pain, offering relief and improved quality of life for countless individuals.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, a chronic pain sufferer, or someone interested in the expansive field of mind-body practices, this study provides invaluable insights. The hope is that with continued research and application, mindfulness meditation will become an accessible, effective therapy for pain management across the board.





